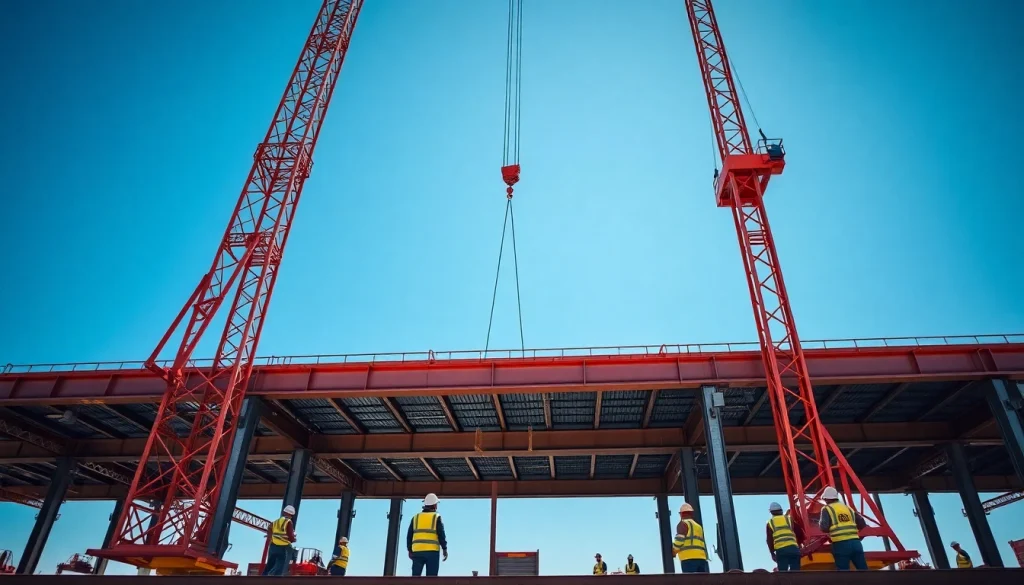
Understanding Structural Steel Installation
Structural steel installation is a critical aspect of the construction industry, providing the backbone for a myriad of structures from skyscrapers to bridges. This installation process involves careful planning, precise execution, and adherence to safety standards. When approached correctly, it can result in strong, durable structures that stand the test of time. For those looking for expert structural steel installation, working with seasoned professionals ensures not only the quality of materials but also the integrity of the final project. Comprehensive knowledge about the process can enhance efficiency and safety at various stages. In this article, we’ll delve deeply into the details surrounding structural steel installation, covering everything from planning to common challenges faced in the field.
What is Structural Steel Installation?
Structural steel installation refers to the process of erecting steel components for buildings or other structures. It encompasses several stages, including fabrication, transportation, and the actual erection of these components on-site. This process combines engineering principles with craftsmanship, ensuring that every piece fits together seamlessly to create a sturdy frame. The installation typically involves a variety of steel sections, including beams, columns, and trusses, which are put together using methods like bolting or welding.
The Importance of Structural Integrity
Structural integrity is a vital consideration in construction and refers to the ability of a structure to withstand its intended load without experiencing failure. Factors such as material specifications, load calculations, and installation practices contribute to overall structural integrity. During the installation of structural steel, meticulous attention must be paid to the alignment and connections of various steel elements. Poorly executed installations can lead to catastrophic failures, costly repairs, and even loss of life.
Common Uses of Structural Steel in Construction
Structural steel is widely used across various construction projects due to its strength, flexibility, and recyclability. Below are some common applications:
- High-Rise Buildings: Skyscrapers are primarily constructed using structural steel because of its ability to support tall, heavy structures while allowing flexibility to withstand lateral forces such as wind.
- Bridges: Steel is a preferred material for bridges due to its durability and resistance to tensile stress, making it ideal for spanning long distances.
- Industrial Facilities: Factories and warehouses often employ steel frames for their ability to accommodate large open spaces without supporting columns.
- Residential Structures: Increasingly, structural steel is being utilized in residential building projects for contemporary designs that require wide open living spaces.
Key Processes in Structural Steel Installation
Preparation and Planning for Steel Erection
Successful structural steel installation begins long before the first beam is set in place. It initiates with comprehensive planning and design analyses. This process includes:
- Site Evaluation: Assessing the site for accessibility, logistics, and existing structures is crucial in determining the approach to installation.
- Detailed Scheduling: Developing a timeline that outlines when materials will arrive and when different phases of installation will occur is essential for maintaining workflow.
- Safety Assessments: Before any work begins, conducting safety assessments helps identify potential hazards on-site and establish protocols to mitigate risks.
Transportation and Delivery of Steel Components
Once planning is complete, the next step involves transporting the fabricated steel components to the construction site. This stage requires attention to detail to ensure that the components arrive on schedule and in perfect condition. Key considerations include:
- Choosing the Right Transport Method: Depending on the size and weight of the steel components, appropriate transportation methods should be selected, ranging from trucks to oversized load carriers.
- Timely Delivery: Coordinate deliveries carefully to prevent delays in the project timeline, ensuring that materials are on site when needed.
- Inspection: Upon arrival, every piece should be inspected for damage before installation, ensuring that only quality materials are used.
Assembly and Erection Techniques
With all plans set and materials on-site, the actual steel installation can commence. This phase consists of precise assembly and erection techniques:
- Sequence of Erection: Steel is typically erected in a specific order, starting with vertical columns followed by beams and trusses. This sequence ensures stability as the structure gains height.
- Use of Cranes and Rigging: Large cranes are used to lift heavy beams and place them in position. Proper rigging techniques are crucial to securing loads and preventing accidents.
- Securing Connections: Connections between steel sections are secured using bolts or welds. It is paramount that these connections meet design specifications to ensure structural integrity.
- Regular Inspections: Implementing ongoing inspections throughout the erection process helps identify any discrepancies in alignment or assembly before they escalate into larger issues.
Best Practices for Safety and Efficiency
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Compliance with local, state, and national safety codes is non-negotiable in structural steel installation. Key standards to adhere to include OSHA regulations and the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) guidelines. Implementing compliance measures involves regular training sessions, thorough documentation, and maintaining safety certifications for all crew members engaged in installation activities.
Safety Gear and Protocols for Workers
The safety of workers is paramount during structural steel installation. Essential personal protective equipment (PPE) includes:
- Hard hats
- High-visibility vests
- Steel-toed boots
- Gloves
- Fall protection harnesses
In addition to PPE, establishing clear safety protocols, such as regular safety meetings, creating emergency response plans, and conducting drills, promotes a culture of safety on the job site.
Utilizing Modern Equipment and Technology
The advancement of technology in construction has transformed the steel installation process, making it more efficient and safer. Incorporating modern tools and equipment, such as:
- 3D Modeling Software: Helps visualize the structural layout before physical installation begins, allowing for better planning and error reduction.
- Robotic Assistance: In some settings, robots assist with welding and other repetitive tasks, increasing precision and reducing the risk of human error.
- Advanced Lifting Equipment: Cranes equipped with load monitoring technology can enhance safety by preventing overload situations.
Challenges Faced During Installation
Weather Conditions and Their Impact
Weather can significantly affect the installation timeline and safety conditions. High winds, rain, snow, and extreme temperatures can pose challenges. Contractors must monitor weather forecasts closely and adjust schedules when necessary. For example:
- Strong winds may necessitate halting work at heights.
- Wet conditions can make surfaces slippery, increasing the risk of falls.
- Cold temperatures may require additional measures to prevent material failures or health risks for workers.
Logistical Considerations on Work Sites
Logistics play a crucial role in ensuring an efficient installation process. Spatial constraints, access routes for equipment, and storage requirements for materials must be planned carefully. Potential logistical challenges include:
- Space limitations on site may hamper crane movements.
- Traffic issues can delay the timely delivery of materials.
- Coordination between multiple trades working simultaneously can lead to scheduling conflicts.
Mitigating Risks in Structural Steel Installation
Risk management is essential to a successful structural steel installation project. Strategies for mitigating risk include:
- The implementation of comprehensive training programs for all workers to minimize human error.
- Regular safety audits to identify and rectify potential hazards before they result in accidents.
- The establishment of an effective communication system among all project stakeholders to ensure everyone is informed about changes and safety protocols.
Case Studies: Successful Structural Steel Projects
Analyzing Notable Commercial Installations
Studying successful structural steel projects provides valuable insights into best practices and approaches that can be replicated. For example, the installation of the US Bank Stadium in Minneapolis showcases excellence in structural steel application. With its complex geometry and extreme loading requirements, the project utilized state-of-the-art design and erection techniques that set new standards in the industry. Lessons learned from this project include the value of collaborative planning among engineers, architects, and contractors.
Lessons Learned from Structural Steel Failures
Failure cases serve as grim reminders of the consequences of negligence in structural engineering. The collapse of the Ronan Point apartment tower in London due to a gas explosion highlighted the critical importance of integrity in structural design. The lessons learned stressed the need for robust safety measures and strict adherence to building codes during construction. By conducting thorough investigations into failure cases, the industry can develop improved practices and standards to prevent future occurrences.
Innovations in Structural Steel Design and Erection
The structural steel industry continues to evolve, with advancements in materials and techniques that enhance performance and sustainability. Innovations such as:
- High-Strength Steels: New alloy compositions have led to high-strength steels that are lighter and more resilient, allowing for slimmer structural designs.
- Prefabrication Techniques: Off-site fabrication speeds up the installation process while ensuring precise assembly, thus minimizing on-site errors.
- Green Steel Options: Increasing emphasis on sustainability has led to the development of eco-friendly steel production methods, which reduce the carbon footprint of structural steel projects.