Understanding Sustainability in Modern Society
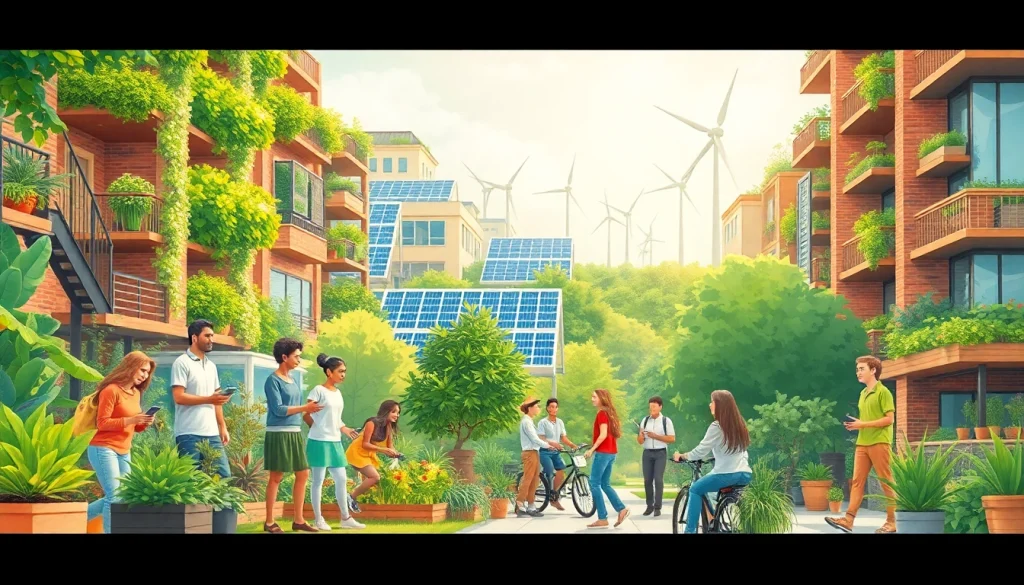
Sustainability is no longer just a trend; it has become a vital aspect of our existence. As the world grapples with climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality, understanding sustainability has emerged as a crucial endeavor. This concept involves meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. By comprehending the depth and breadth of sustainability, individuals and communities can engage in practices that promote a healthier planet and a more equitable society. For those seeking to enhance their understanding, resources and insights are available at https://www.unsustainablemagazine.com, which offers comprehensive information on climate, equality, and sustainable living.
Defining Sustainability and Its Importance
Sustainability is often defined through three pillars: environmental integrity, economic viability, and social equity. Each pillar is interlinked and essential for fostering a stable ecosystem that protects both nature and humanity. Environmental sustainability emphasizes the need to protect our natural resources and biodiversity. Economic sustainability stresses the importance of sustainable economic growth without damaging the environment or social systems. Lastly, social sustainability advocates for equitable distribution of resources and opportunities across all societal segments. Understanding these definitions is crucial because they outline the framework through which we can all contribute to a sustainable future.
Key Areas of Focus: Environment, Economy, and Society
The interconnectedness of the environment, economy, and society creates a holistic view of sustainability. In environmental terms, sustainability calls for preserving ecosystems and biodiversity. This requires effective management of natural resources, as well as shifting toward renewable energy sources to limit our reliance on fossil fuels. Economically, it emphasizes the need for economic activities to meet present needs today while securing resources for future generations. Lastly, social sustainability tackles challenges such as inequality, ensuring that all people have access to the benefits of a sustainable society, including education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
The Role of the Individual in Sustainable Choices
Individuals play a pivotal role in promoting sustainability through their daily choices. Personal actions, such as reducing waste, conserving energy, and supporting local and sustainable businesses, contribute significantly to broader sustainability goals. Educating oneself about environmental issues and advocating for change within community spheres amplifies these efforts. By making conscious choices, individuals can inspire others to embrace sustainable living, generating a ripple effect that encourages widespread change. Engaging in community sustainability initiatives, whether through volunteering or simply spreading awareness, helps foster a culture that prioritizes sustainability.
Sustainable Practices for Everyday Life
On the path to sustainability, personal practices can make a substantial difference. Adopting sustainable practices at home not only reduces one’s carbon footprint but also enhances overall well-being. From minimizing waste to embracing renewable energy, these framework practices can collectively reduce our environmental impact.
Zero Waste Living Explained
Zero waste living focuses on minimizing waste to landfill and has gained traction as a practical approach to sustainability. This lifestyle encourages individuals to reduce their consumption and find ways to reuse, recycle, or repurpose materials. By refusing single-use plastics, opting for bulk purchasing, and composting organic waste, individuals can significantly reduce the amount of waste they generate. One of the key principles is the “Five R’s”: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, and Rot. Embracing zero waste may seem daunting initially, but small, consistent changes can lead to a more sustainable lifestyle. For instance, understanding how to create a waste audit can help assess personal waste types and identify reduction opportunities.
Eco-Friendly Transportation Options
Transportation plays a critical role in carbon emissions, making it one of the major contributors to climate change. Eco-friendly transportation options include public transportation, cycling, walking, carpooling, and the use of electric or hybrid vehicles. Individuals can explore local public transit systems that offer affordable and less polluting alternatives to driving. Bicycle-sharing programs and safe cycling paths in urban areas encourage biking as a convenient option for short distances. By promoting mixed-use developments and walkable neighborhoods, cities can foster environments where residents feel comfortable using eco-friendly transportation means, thus lowering the overall carbon footprint.
Adopting Renewable Energy at Home
One of the most impactful ways to live sustainably is by adopting renewable energy sources at home. This transition can be achieved by installing solar panels, utilizing wind turbines, or harnessing geothermal energy. Making the shift to renewable energy helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels and lessens greenhouse gas emissions. Many governments also offer incentives for homeowners who invest in renewable energy systems, making it not only an environmentally sound choice but also a financially beneficial one. Educational resources and case studies can guide families through the process of evaluating their energy needs, budgeting for renewable sources, and understanding local regulations.
The Impact of Sustainable Design
Sustainable design goes beyond aesthetics; it is a philosophy that seeks to minimize environmental impact while enhancing quality of life. This design approach integrates principles that respect not only the environment but also the communities that inhabit these spaces. By adopting sustainable design practices, architects and urban planners can create structures and spaces that utilize resources efficiently while meeting the needs of inhabitants.
Architectural Innovations Supporting Sustainability
Architectural innovations have led to groundbreaking designs that exemplify sustainability. Features such as green roofs, efficient insulation, and rainwater harvesting systems merge functionality with environmental consciousness. Building designs may also incorporate sustainable materials, such as bamboo or reclaimed wood, which have a lower environmental impact than traditional materials. An exemplary case includes net-zero energy buildings that generate as much energy as they consume through smart design and technology. These innovations not only enhance energy efficiency but also provide healthier living spaces for occupants.
Green Spaces and Urban Planning
Urban planning has a significant impact on community sustainability. Integrating green spaces—parks, community gardens, and green roofs—can enhance urban environments by providing essential ecosystems and recreation opportunities. Well-planned green spaces promote biodiversity, improve air quality, reduce urban heat, and foster community interactions. Cities can enhance sustainability by implementing policies that prioritize urban forests and protected green areas, fostering ecological resilience, and promoting a sense of community among residents.
Products That Promote Sustainable Lifestyles
Consumer choices are pivotal in driving the market toward sustainability. Products designed with environmental considerations include biodegradable packaging, energy-efficient appliances, and sustainably sourced materials. Brands that adopt sustainable practices in their supply chain and production methods are gaining recognition, helping consumers make informed choices. When individuals support these companies, they not only choose products with lower environmental footprints, but they also encourage more businesses to adopt sustainable practices. This shift in consumer behavior can lead to significant changes in manufacturing processes across industries.
Global Movements and Initiatives
The importance of collective action in promoting sustainability cannot be overstated. Global movements, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), provide a strategic framework for sustainable development from multiple fronts, including poverty alleviation, climate action, and gender equality. These initiatives work to create networks of activists, non-profits, and government agencies committed to fostering a more sustainable world.
Highlighting Activism Around Climate Change
Activism has become a crucial element in the fight against climate change. Individuals and organizations dedicate themselves to raising awareness and advocating for policy changes to combat global warming. Grassroots movements, online campaigns, and public demonstrations play significant roles in mobilizing communities for climate action. Activists stress the urgency of addressing climate change and its effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. By participating in local and international climate strikes, volunteers support a larger movement geared towards comprehensive environmental reforms.
International Partnerships for Sustainability
International partnerships function as a backbone for global sustainability efforts. Collaborative initiatives, such as the Paris Agreement, illustrate how nations can come together to address climate change. These partnerships foster the sharing of resources, knowledge, and innovative practices that benefit various sectors working toward sustainability. From funding renewable projects in developing countries to sharing technologies that reduce emissions, international collaborations are fundamental in addressing the worldwide dimensions of environmental degradation and social injustice.
Community Initiatives Making a Difference
Communities around the globe are developing innovative initiatives to tackle local sustainability challenges. These grassroots movements often bring residents together, fostering collaboration and education. Community-supported agriculture (CSA), local recycling programs, and neighborhood energy efficiency initiatives are prime examples of how collective efforts can yield significant environmental benefits. Additionally, these initiatives empower individuals by promoting self-sufficiency and resilience, while improving local food systems and economies. By harnessing local knowledge and resources, communities can create viable sustainability solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Measuring the Success of Sustainability Efforts
Measuring the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives is vital to understanding their impact and guiding future actions. Various methodologies exist to evaluate performance, emphasizing the need for transparent metrics to track progress. Establishing benchmarks, metrics, and case studies helps communities assess their sustainable development efforts consistently.
Key Performance Indicators for Sustainable Projects
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential for measuring success in sustainability projects. These metrics allow organizations to evaluate their environmental, economic, and social impacts systematically. Common examples include tracking carbon emissions reductions, energy consumption, waste diversion rates, and community engagement levels. By regularly analyzing these KPIs, organizations can not only gauge progress but also identify areas for improvement. Implementing effective reporting mechanisms and utilizing technology in data collection further augments the accountability of sustainability efforts.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation
Case studies serve as invaluable resources for understanding successful implementations of sustainability initiatives. By examining these real-world examples, stakeholders can draw lessons, develop best practices, and gain insights into overcoming common challenges. From cities that have successfully transitioned to renewable energy sources to corporations that have minimized their waste outputs, each case study highlights unique approaches to sustainability. Compiling these successful narratives and sharing them within communities can inspire further action and innovation.
Challenges and Future Directions in Sustainability
Despite the progress made in sustainability efforts, significant challenges persist. These include overcoming resistance to change, securing funding, and addressing systemic inequalities that complicate access to sustainable solutions. Future directions must also consider the impact of technological innovation on sustainability. Emerging tools and techniques can enable more efficient resource use and enhance awareness regarding environmental consequences. Stakeholders must balance the drive for innovation with the need to ensure that solutions are accessible, equitable, and environmentally sound. Crafting inclusive policies that engage diverse populations while addressing global sustainability challenges is crucial for fostering a sustainable future.